Last updated March 28, 2025
In this guide, we walk you through the process of migrating your Postgres database from Azure Database to Heroku Postgres. This guide uses Azure Storage to store the database dump file. Before starting the migration, make sure you completed the steps from Preparing Your Migration to Heroku Postgres.
Get Your Database Size
In most cases, the dump and restore strategy for migration is suitable if your database size is less than 100 GB. With Azure, there are multiple ways to determine your database size. When you select your database from the list of Azure resources, navigate to Monitoring > Metrics, and select the Database Size metric for the chart.
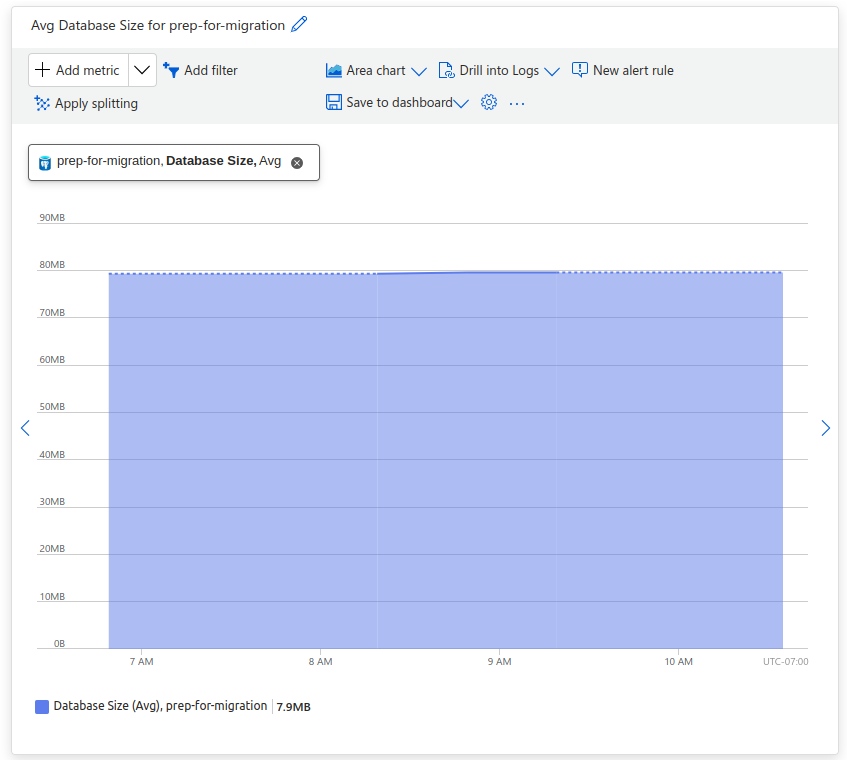
In the example, our database size is just under 80 MB.
For a more accurate size reading, connect to your database instance and use the list databases \l+ command. Navigate to Settings > Connect to find your connection details.
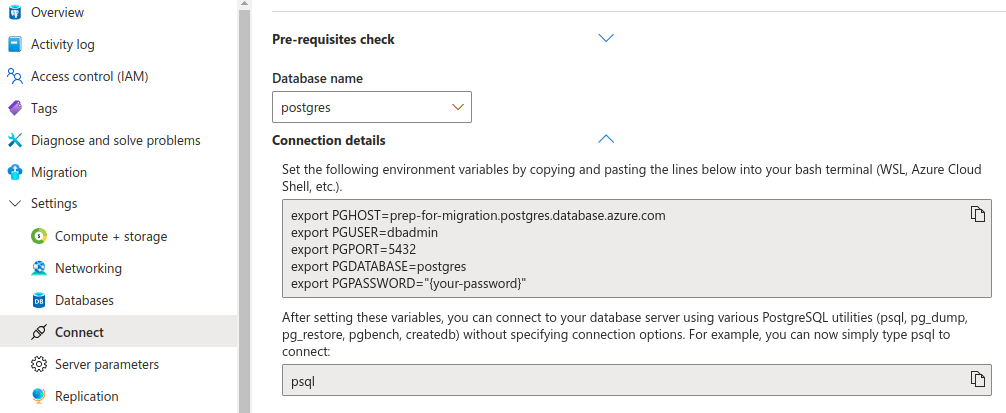
The various export statements show your database connection string values. The connection string for using the psql client uses the format:
postgres://DB_USERNAME:DB_PASSWORD@DB_HOST:DB_PORT/DB_NAME
For Azure databases, you set the database admin username and password on initial database creation.
Our example database is called postgres, so we connect our database to the psql client with:
$ psql postgresql://dbadmin:mypassword@prep-for-migration.postgres.database.azure.com:5432/postgres
After connecting, you can show the database size with the list databases \l+ command:
$ psql=> \l+
List of databases
Name | Owner | Encoding | Collate | Size |
----------------+----------+----------+-------------+--------+
postgres | postgres | UTF8 | en_US.UTF-8 | 76 MB |
The Size column shows our database size is 76 MB.
See Choosing the Right Heroku Postgres Plan for which Heroku Postgres plan fits your database size.
Prepare the Database Dump
Before starting, either set your system to read-only mode, or bring all your dependent services offline and notify end users of the current maintenance status.
If your database is attached to a Heroku app, put your app in maintenance mode.
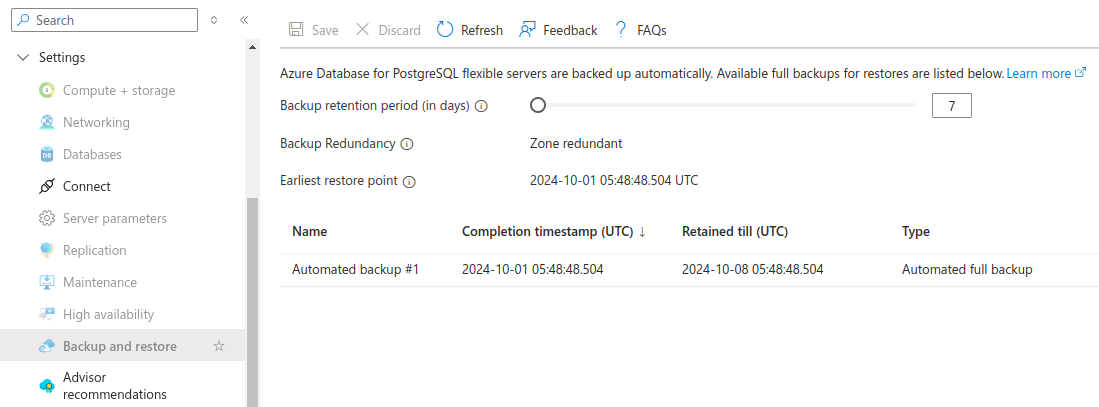
Back Up Your Database
Before performing the migration, make sure you have a recent backup of your database on Azure. Navigate to Settings > Backup and restore. You see a list of recent backups, which Azure performs and retains automatically for you.
Dump the Database to a Local File
Using pg_dump, dump your Azure database to a local file:
$ pg_dump postgres://DB_USERNAME:DB_PASSWORD@DB_HOST:DB_PORT/DB_NAME \
-Fc -b -v \
-f /tmp/data-for-migration.sql
The time it takes to run this command varies depending on the size of your database. You can keep an eye on the file size of /tmp/data-for-migration.sql to verify that the long process is running.
Upload the File to Azure Storage
Heroku can restore a Postgres database from a file that’s accessible via a URL. For this migration from Azure Database for PostgreSQL, you can upload your data backup file to Azure Storage, then obtain a signed URL for that file.
First, create a blob container. In our example, we named our bucket postgres-for-migration.

For security, make sure to set the access level for your container to Private (no anonymous access).
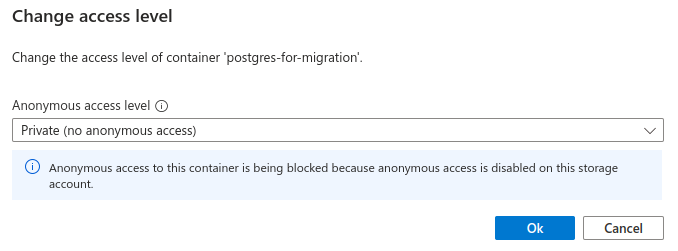
Azure Storage automatically encrypts your data at rest.
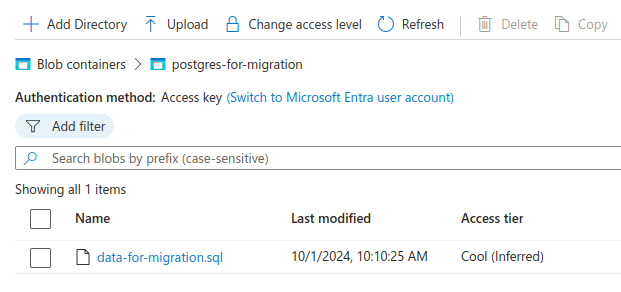
After creating your blob container, upload the /tmp/data-for-migration.sql file from the Dump the Database to a Local File step.
Perform the Restore Migration
Create a Heroku app
Use the Heroku CLI to log into your Heroku account.
$ heroku login
Next, create a Heroku app and provide a name for it, such as postgres-migration-from-azure.
$ heroku apps:create psql-migration-from-azure
Creating ⬢ psql-migration-from-azure... done
Create the Heroku Postgres Add-on
After creating your Heroku app, add the Heroku Postgres add-on with an appropriate plan. Based on the database information from Get Your Database Size, we use the Essential-1 Postgres plan.
$ heroku addons:create \
--app psql-migration-from-azure \
heroku-postgresql:essential-1
Creating heroku-postgresql:essential-1 on ⬢ psql-migration-from-azure... ~$0.013/hour (max $9/month)
Database should be available soon
postgresql-clear-97314 is being created in the background. The app will restart when complete...
Use heroku addons:info postgresql-clear-97314 to check creation progress
Use heroku addons:docs heroku-postgresql to view documentation
Heroku begins provisioning a Postgres database for your Heroku app, providing a unique name. Within a few minutes, you can run the following command with the database to see the created database.
$ heroku addons:info postgresql-clear-97314
=== postgresql-clear-97314
Attachments: psql-migration-from-azure::DATABASE
Installed at: Tue Oct 01 2024 11:00:00 GMT-0700 (Mountain Standard Time)
Max Price: $9/month
Owning app: psql-migration-from-azure
Plan: heroku-postgresql:essential-1
Price: ~$0.013/hour
State: created
Install Necessary Extensions for Heroku Postgres
Before migrating data, install any extensions you had in your Azure database instance.
First, to see what extensions are already installed on your Heroku Postgres instance, connect to your Heroku Postgres instance with pg:psql:
$ heroku pg:psql --app psql-migration-from-azure
--> Connecting to postgresql-clear-97314
psql (16.4 (Ubuntu 16.4-1.pgdg20.04+1), server 16.2)
SSL connection (protocol: TLSv1.3, cipher: TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384, compression: off)
Type "help" for help.
psql=> \dx
List of installed extensions
Name | Version | Schema | Description
--------------------+---------+------------+-------------------------------
pg_stat_statements | 1.10 | public | track planning and executio...
plpgsql | 1.0 | pg_catalog | PL/pgSQL procedural language
(2 rows)
Install any extensions you had at Azure that aren’t already in Heroku Postgres. From our example, we need the tablefunc and uuid-ossp extensions.
$ psql=> CREATE EXTENSION IF NOT EXISTS tablefunc;
CREATE EXTENSION
psql=> CREATE EXTENSION IF NOT EXISTS "uuid-ossp";
CREATE EXTENSION
psql=> \dx
List of installed extensions
Name | Version | Schema | Description
--------------------+---------+------------+-------------------------------
pg_stat_statements | 1.10 | public | track planning and execution…
plpgsql | 1.0 | pg_catalog | PL/pgSQL procedural language
tablefunc | 1.0 | public | functions that manipulate…
uuid-ossp | 1.1 | public | generate universally unique…
(4 rows)
See Extensions, PostGIS, and Full Text Search Dictionaries on Heroku Postgres for supported extensions and how to install them.
Get the Signed URL For the File in Azure Storage
Next, restore all the data from your pg_dump backup to your new Heroku Postgres database. For this, you need a URL that points to your backup file. In Azure Storage, create a shared access signature (SAS).
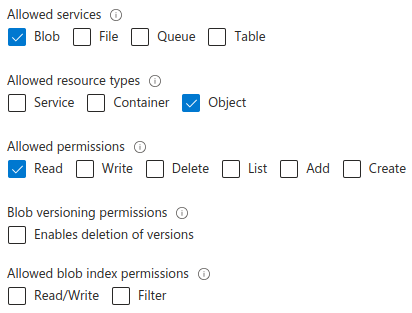
Make sure the SAS you create is for Blob services and Object resource types, and that it has Read permissions.
Set a reasonable expiration start and end period, such as a window over the next hour. Finally, click Generate SAS and connection string.
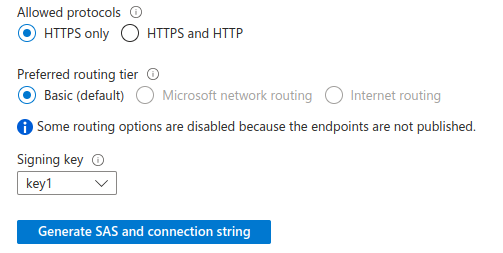
You now see the Blob service SAS URL, which provides access to your Azure Storage root folder. It looks similar to this example:
https://myazureobjectstorage.blob.core.windows.net/?sv=2022-11-02&ss=b&srt=o&sp=r&se=2024-10-02T01:23:25Z&st=2024-10-01T17:23:25Z&spr=https&sig=mPrWUfttKrIOP5lkUQh8kd8PY7ZhXbL3WCqj5YbhpjU%3D
The domain matches the name of your Azure storage account. In our case, it’s myazureobjectstorage.blob.core.windows.net. After the domain, append the name of your container and the file you want to access. Then, add on all of the query parameters which include the signature.
In our example, the signed URL for our database dump file is:
https://myazureobjectstorage.blob.core.windows.net/postgres-for-migration/data-for-migration.sql?sv=2022-11-02&ss=b&srt=o&sp=r&se=2024-10-02T01:23:25Z&st=2024-10-01T17:23:25Z&spr=https&sig=mPrWUfttKrIOP5lkUQh8kd8PY7ZhXbL3WCqj5YbhpjU%3D
Restore on Heroku
Now that you have the presigned URL, use the Heroku pg:backups:restore command to restore your Heroku Postgres database from your file in Azure Storage. The command looks like:
$ heroku pg:backups:restore 'AZURE-SIGNED-URL-IN-QUOTES' \
--app psql-migration-from-azure \
--confirm psql-migration-from-azure
Use Ctrl-C at any time to stop monitoring progress; the backup will continue restoring.
Use heroku pg:backups to check progress.
Stop a running restore with heroku pg:backups:cancel.
Starting restore of [AZURE-SIGNED-URL] to postgresql-clear-97314... done
Restoring... done
Keep in mind with this command:
- When you paste in your Azure-signed URL, make sure to contain it within quotes.
- Provide the
--appargument to tell Heroku which application and corresponding database you want to operate on. - This command is destructive, requiring you to confirm it. If you don’t provide the
--confirmargument, you’re asked to confirm the action before continuing.
Migrate Any Custom Settings
Just as you saved your Azure database configurations to a file called /tmp/settings_postgres.csv, you can do the same for your Heroku Postgres configuration with the command:
$ heroku pg:psql --app psql-migration-from-azure \
-c "\copy (select * from pg_settings) to '/tmp/settings_heroku.csv' with (format csv, header true);"
Compare your Heroku Postgres settings with your Azure database settings. Find any configurations from your Azure setup and reapply them to your Heroku Postgres instance.
Testing and Verifying a Successful Migration
We recommend testing to verify that data has migrated over successfully. Testing can include:
- Comparing table counts between the two databases.
- Comparing row counts for every table between the two databases.
- Comparing query results between the two databases.
- Running various acceptance tests on your new database, validating proper behavior and performance.
Connecting Existing Applications and Services
After verifying that the database migration was successful, point your existing applications and services to the new database.
Get Heroku Postgres Credentials
When you create the Heroku Postgres add-on, Heroku automatically configures a new environment variable called DATABASE_URL, which contains the credentials and connection information for your new database. Run the heroku config:get command to fetch the variable:
$ heroku config:get DATABASE_URL --app psql-migration-from-azure
postgres://u53ijh9udlpj3m:p5018c7e2c6db5882d6b7a09914b27cc0114443dd427dd5f62c1e6b83ed1f099c@c2ihhcf1divl18.cluster-czrs8kj4isg7.us-east-1.rds.amazonaws.com:5432/d9ad4c48p98fc6
You can also find your credentials with the heroku:pg:credentials command.
The Postgres URI follows this format, so that you can parse the individual pieces:
postgres://DB_USERNAME:DB_PASSWORD@DB_HOST:DB_PORT/DB_NAME
Update Dependent Systems and Test
Update your existing systems to point to Heroku Postgres with this information. Test each system to make sure the connection is successful.
Wrap-up
Now that your applications and services are pointing to Heroku Postgres and running as expected, you can close the maintenance window and restore full availability to your end users.
When you’re confident that the migration is successful and you no longer need your Azure database, you can delete it completely.
With your migration complete, you can now enjoy the flexibility and low-cost convenience of Heroku Postgres. See our Heroku Postgres documentation for more information on using your database.